BARIUM FLUORIDE, BaF2
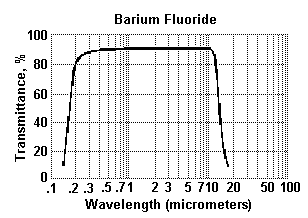
Barium Fluoride is used for optical windows, lenses and prisms particularly when transmission into the ultraviolet is desired. The transmission range is 0.2 µm - 11 µm. Transmission in the VUV is degraded by prolonged exposure to moist atmosphere, but it is not significantly degraded under high energy irradiation. Barium fluoride is less resistant to attack by water than Calcium Fluoride. Pronounced water attack occurs at 500 °C, but the material can be used to 800 °C in a dry environment. Barium fluoride is the most resistant fluoride to high energy radiation, but does not have VUV transmission of the other fluorides. The material is relatively hard but is highly sensitive to thermal shock. Maximum available size: 180 mm Dia x 40 mm Thk.
|
Main Properties |
||||||||||||||
|
Chemical Formula |
BaF2 |
|||||||||||||
|
Crystal Class |
Cubic |
|||||||||||||
|
Molecular Weight |
175.36 |
|||||||||||||
|
Lattice Constant, Å |
6.196 |
|||||||||||||
|
Density, g/cm3 (20 °C) |
4.89 |
|||||||||||||
|
Knoop Hardness, kg/mm2 |
82 |
|||||||||||||
|
Young's Modulus, GPa |
53.05 |
|||||||||||||
|
Shear Modulus, GPa |
25.4 |
|||||||||||||
|
Bulk Modulus, GPa |
56.4 |
|||||||||||||
|
Apparent Elastic Limit, MPa |
26.89 |
|||||||||||||
|
Poisson Ratio |
0.343 |
|||||||||||||
|
Dielectric Constant for 2 x 106 Hz |
7.33 |
|||||||||||||
|
Melting Temperature, K |
1550 |
|||||||||||||
|
Specific Heat, cal/(g K) at 274 K |
0.096 |
|||||||||||||
|
Thermal Conductivity, W/(m K) at 286 K |
11.7 |
|||||||||||||
|
Thermal Expansion, 1/K at 300 K |
19.9 x 10-6 |
|||||||||||||
|
Bandgap, eV |
9.1 |
|||||||||||||
|
Solubility, g/100 g H2O |
0.17 |
|||||||||||||
|
Refractive Index |
||||||||||||||
|
Wavelength, µm |
0.26 |
0.30 |
0.36 |
0.48 |
0.85 |
3.24 |
5.14 |
6.50 |
8.00 |
8.60 |
9.20 |
9.80 |
||
|
Refractive Index |
1.51 |
1.50 |
1.49 |
1.48 |
1.47 |
1.46 |
1.45 |
1.44 |
1.43 |
1.42 |
1.41 |
1.40 |
||